Geo-Thermal Skyscrapers: The Future of Energy-Independent Commercial Buildings
As urban landscapes evolve, so does the need for sustainable energy solutions. Among the most promising innovations in green architecture is the concept of geothermal skyscrapers, high-rise buildings that harness the Earth’s natural heat for energy independence. This approach offers an environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and efficient alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources. As commercial buildings continue to expand in height and complexity, integrating geothermal technology into skyscrapers can pave the way for a cleaner and more energy-efficient future.
Understanding Geothermal Energy: Using the Earth to Heat Buildings and Generate Electricity
Geothermal energy is derived from the heat stored beneath the Earth’s surface. The planet’s core generates immense thermal energy due to radioactive decay and residual heat from Earth’s formation. This energy manifests in the form of hot water, steam, or simply high subterranean temperatures, which can be captured and used for various applications, including heating, cooling, and electricity generation.
There are three primary forms of geothermal energy utilization:
- Geothermal Power Plants – These facilities extract steam or hot water from underground reservoirs to spin turbines and generate electricity.
- Direct Use Systems – These systems tap into naturally occurring hot water sources for heating purposes.
- Ground Source Heat Pumps (GSHPs) – These pumps use stable underground temperatures to heat and cool buildings.
In the context of geothermal skyscrapers, the focus is mainly on GSHPs and direct-use systems, which can significantly reduce energy consumption and reliance on fossil fuels.
Can Geothermal Energy Heat Buildings?
Yes, geothermal energy is a highly effective and reliable method for heating buildings, including skyscrapers. Unlike traditional heating systems that rely on burning fossil fuels, geothermal heating leverages the Earth’s stable underground temperatures to provide consistent indoor climate control.
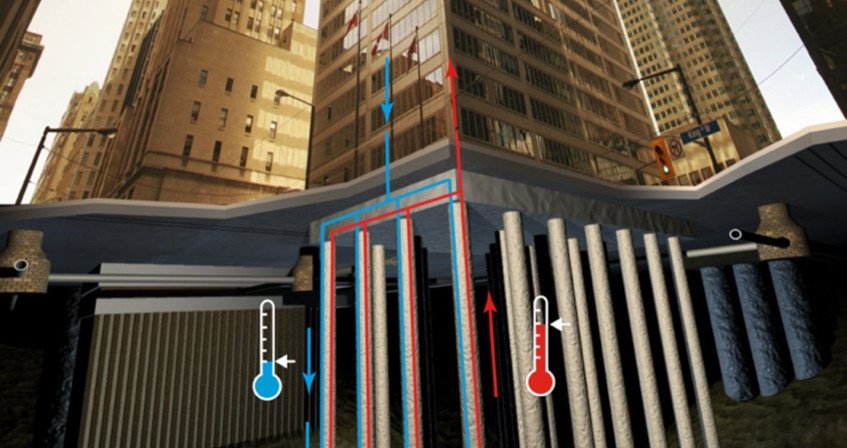
How Geothermal Heating Works in Skyscrapers
In a geothermal skyscraper, heat exchange occurs through a network of underground pipes, known as a geothermal loop system. This system consists of:
- Vertical Boreholes – Deep wells drilled hundreds or even thousands of feet into the Earth.
- Heat Exchangers – Pipes filled with a heat-transfer fluid, such as water or antifreeze, circulate underground to absorb heat.
- Heat Pumps – These devices transfer the captured heat into the building’s heating system.
During colder months, the system draws heat from the Earth and distributes it throughout the skyscraper. In warmer months, the process is reversed, with the heat pump extracting warmth from the building and dissipating it into the ground, effectively cooling the interior spaces.
Geothermal heating in skyscrapers provides a consistent and sustainable source of warmth while dramatically reducing the building’s reliance on external energy sources.
What is the Downside of Geothermal Heating?
While geothermal heating offers numerous benefits, there are some challenges associated with its implementation in skyscrapers:
- High Initial Costs – Drilling boreholes and installing the necessary infrastructure for geothermal heating is expensive. However, these costs are often offset over time through energy savings.
- Site-Specific Constraints – Not all locations are suitable for geothermal systems. Geological conditions, soil composition, and underground temperature gradients must be favorable.
- Space Requirements – While vertical boreholes minimize the footprint, deep drilling can still pose logistical challenges in urban environments.
- Installation Complexity – Retrofitting existing skyscrapers with geothermal systems is more challenging than incorporating the technology into new construction.
- Potential for System Degradation – Over time, components such as heat pumps and underground pipes may require maintenance or replacement.
Despite these downsides, technological advancements and increasing adoption of geothermal systems continue to address these challenges, making them more viable for widespread use.
How Effective is Geothermal Heating?
Geothermal heating is one of the most efficient heating technologies available. It provides a reliable, year-round source of energy that can significantly reduce operational costs and carbon footprints.
Efficiency and Performance
- Energy Savings – Geothermal heat pumps can achieve efficiency ratings of 300-600%, meaning they produce three to six times more energy than they consume.
- Long-Term Cost Benefits – While the initial installation cost is high, long-term savings on energy bills make geothermal systems a financially attractive investment.
- Environmental Impact – Geothermal energy is renewable, producing minimal greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional heating methods.
- Longevity – Geothermal systems have a long lifespan, with underground piping lasting up to 50 years and heat pumps typically functioning for 20-25 years.
The Future of Geothermal Skyscrapers
As urban centers grow and the demand for energy-efficient buildings increases, geothermal skyscrapers represent the next frontier in sustainable architecture. Advances in drilling technology, energy storage, and hybrid geothermal systems are making this approach more accessible and cost-effective.
Innovative Approaches to Geothermal Skyscrapers
- Hybrid Systems – Combining geothermal energy with solar panels, wind turbines, and energy-efficient building materials can further enhance sustainability.
- Smart Grid Integration – Geothermal skyscrapers equipped with smart sensors can optimize energy use and dynamically adjust heating and cooling based on occupancy and external temperatures.
- Modular Geothermal Units – Prefabricated geothermal units can streamline installation and reduce costs.
Geothermal skyscrapers offer a promising path toward energy independence for commercial buildings. By leveraging the Earth’s natural heat, these buildings can achieve significant energy savings, reduce carbon emissions, and contribute to a more sustainable future. While challenges exist, ongoing advancements in technology and design are paving the way for wider adoption of geothermal energy in high-rise construction. As cities strive to meet climate goals and reduce reliance on non-renewable energy sources, geothermal skyscrapers stand as a beacon of innovation in sustainable urban development. image/encyclopedie-environnement





